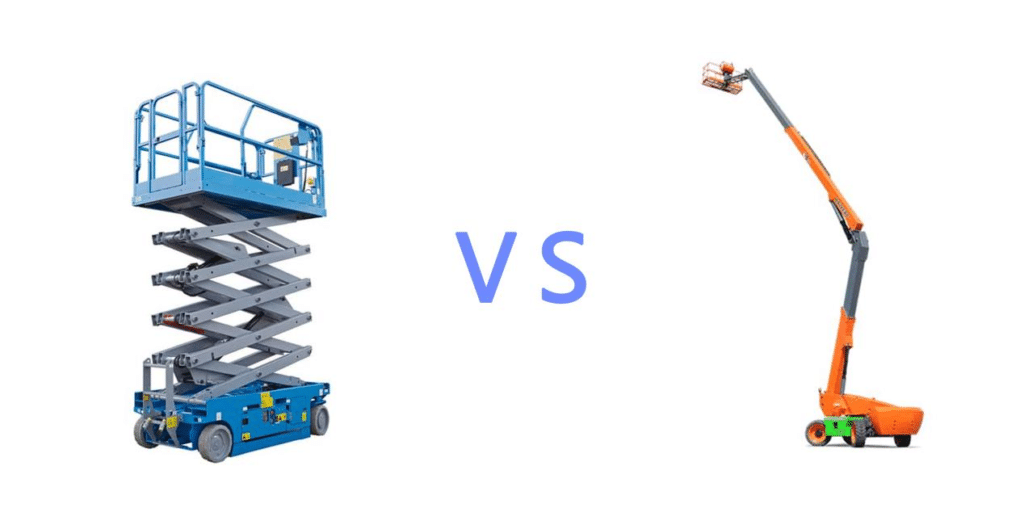
Scissor Lifts vs Boom Lifts, what is the difference?
Concept of the Scissor Lifts & Boom Lifts
Aerial Working Platform that serves various industries in high-altitude operations, equipment installation, maintenance, and other mobile high-altitude operations.
Aerial work platform is a mobile high-altitude operation product that serves various industries in high-altitude operations, equipment installation, maintenance, and other mobile high-altitude operations.
The main products related to high-altitude work platforms include: Boom Lifts vs. Scissor Lifts
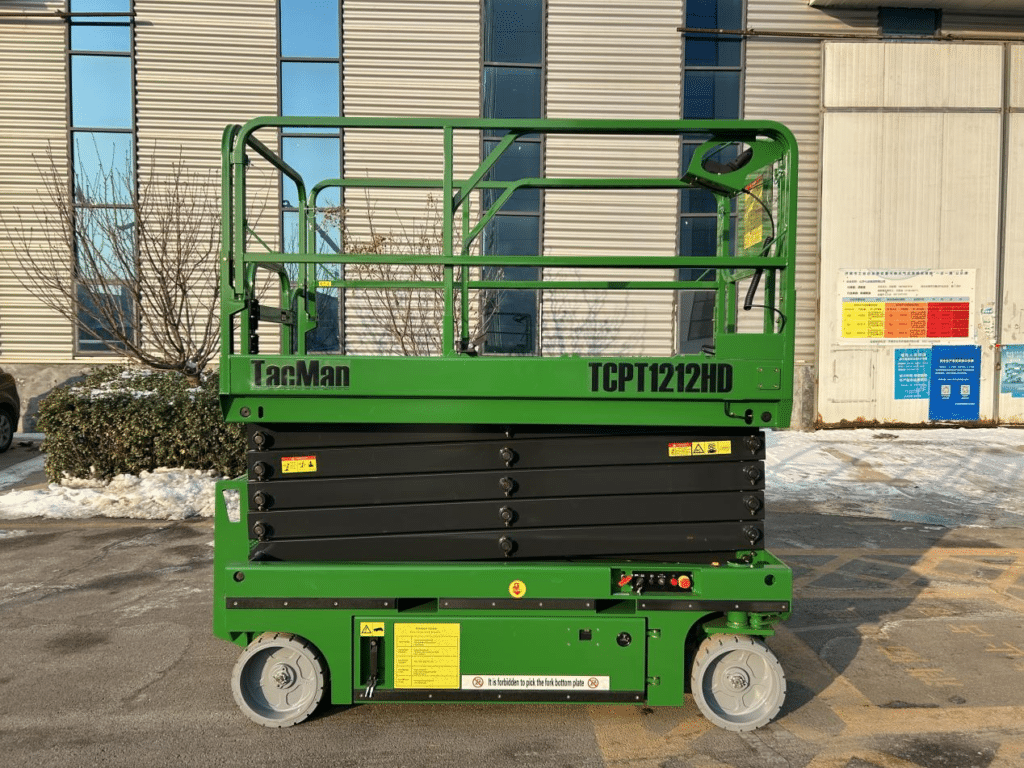
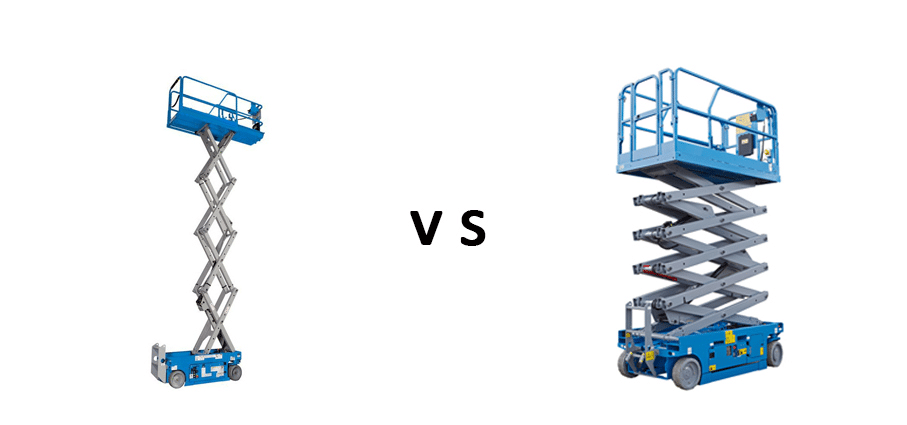
Scissor Lifts
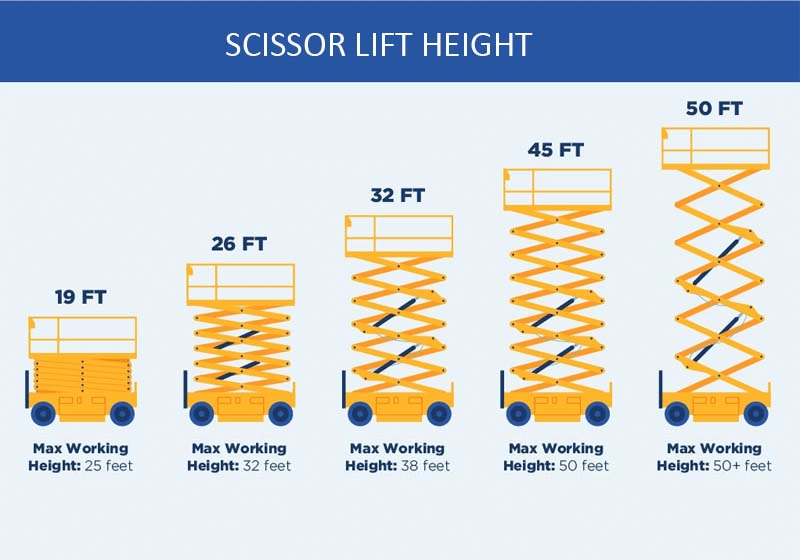
The Scissor Lifts is a widely used specialized equipment for high-altitude operations. Its scissor-type mechanical structure provides high stability for the lifting platform after lifting, with a wide working platform and high load-bearing capacity, making the range of high-altitude operations larger and suitable for multiple people working simultaneously. It makes high-altitude operations more efficient and safer.
Features:
- The lifting mechanism is made of high-strength manganese steel giant tubes.
- Equipped with safety protection devices to prevent overloading of the lifting platform.
- Equipped with a safety protection valve to prevent hydraulic pipeline rupture.
- Equipped with emergency descent devices in case of power outage.
This product is suitable for mobile high-altitude operations such as installation and maintenance of high-altitude equipment in various industries. According to different requirements, different power forms can be selected (such as three-phase AC power supply, single-phase AC power supply, DC power supply, and internal combustion power supply, etc.), and manual hydraulic devices can be added. It can work normally in places with power outages or no power supply, and a telescopic platform can be added.
When the platform length is not enough, it can be extended to the desired position, thereby improving work efficiency. It is an ideal equipment product for modern tall buildings and equipment and is essential for high-altitude safety and civilized production.
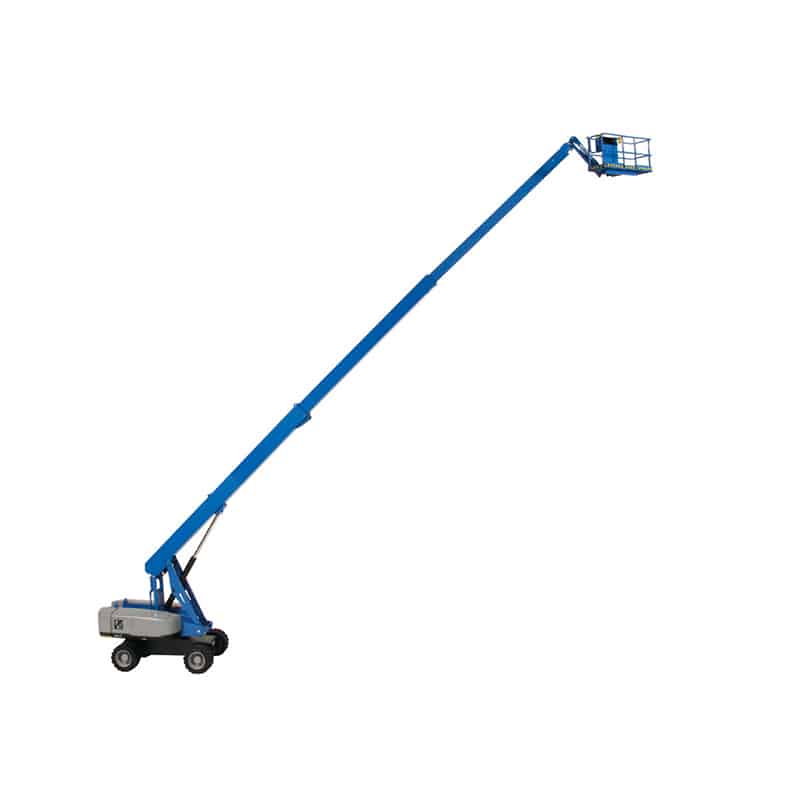
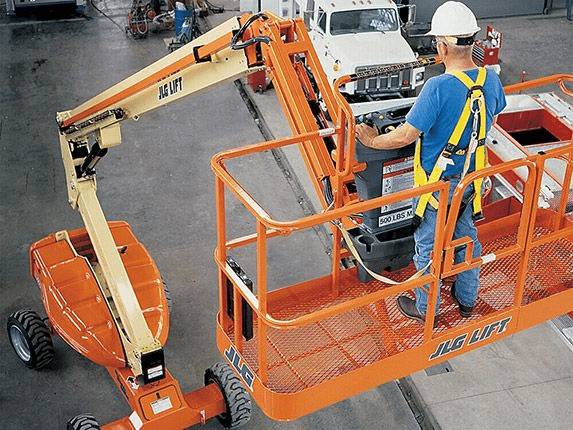
Boom Lifts
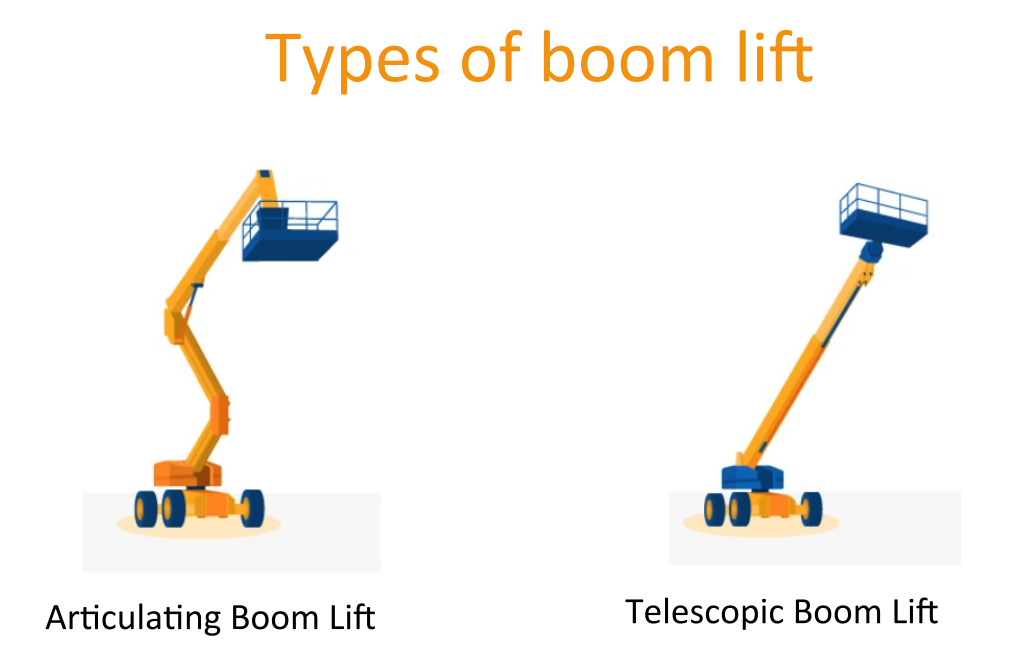
According to the arm extension method, it can be divided into two types: Telescopic Boom Lift & Articulated Boom Lift. It is mostly used in places with high height requirements such as shipyards. This type of machine has good safety and is easy to move, but the cost is high.
At present, there are four types of high-altitude work vehicles mainly used in the market: scissor fork type, straight arm type, curved arm type, and vehicle-mounted type. What are the suitable situations for each type of vehicle? Let me explain the characteristics of these models to everyone.
Application of the Scissor Lifts vs Boom Lifts
Scissor Lifts
Telescopic Boom Lift
Articulated Boom Lift
Additionally, there is an vehicle mounted high-altitude work platform.
With the above introduction, everyone can also better choose suitable products.
Telescopic Boom Lift
Purchasing Tips
With the development of social science and technology, whether it is architecture, civil engineering, or people’s daily lives, high-altitude work platforms are indispensable. Many businesses seize this opportunity and invest in building factories, and lifting machinery companies are standing like bamboo shoots in major industrial cities.
However, the lifting and lowering machinery industry is still booming and in short supply. From the side, it can be seen that the rapid development of society has driven the development of the entire industry and people’s needs. However, as buyers, how to choose good lifting machinery from the numerous company products has become an important topic today.
Working Principle
Hydraulic oil is formed by a vane pump to form a certain pressure, which enters the lower end of the hydraulic cylinder through an oil filter, explosion-proof electromagnetic directional valve, throttle valve, hydraulic control one-way valve, and balance valve, causing the piston of the hydraulic cylinder to move upwards and lift heavy objects. The return oil from the upper end of the hydraulic cylinder returns to the oil tank through the explosion-proof electromagnetic directional valve, and its rated pressure is adjusted through the overflow valve. The pressure reading on the pressure gauge is observed.
The piston of the hydraulic cylinder moves downwards (i.e. the weight is lowered). Hydraulic oil enters the upper end of the hydraulic cylinder through an explosion-proof electromagnetic directional valve, and the return oil from the lower end of the hydraulic cylinder returns to the oil tank through a balance valve, hydraulic control one-way valve, throttle valve, and explosion-proof electromagnetic directional valve.
To ensure stable descent of heavy objects and safe and reliable braking, a balance valve is installed on the return oil circuit to balance the circuit and maintain pressure, so that the descent speed is not affected by heavy objects. The flow rate is adjusted by the throttle valve to control the lifting speed. To ensure safe and reliable braking and prevent accidents, a hydraulic control one-way valve, also known as a hydraulic lock, is added to ensure safe self-locking in the event of an accidental rupture of the hydraulic pipeline. An overload sound control alarm has been installed to distinguish between overloading or equipment failure.
Operating Standards TacMan
- Professional operators who have undergone specialized training, passed exams, and hold certificates must be assigned to work.
- Operators must follow the maintenance regulations of mechanical equipment and carry out various inspections and maintenance before starting the lifting platform. Before starting work, the working range of the platform vehicle should be checked, and obstacles that hinder the rotation and walking of the platform vehicle should be removed.
- Support is an important preparatory work for the operation of high-altitude work platforms, and a flat ground should be selected. If the foundation is soft or uneven, it must be padded with sleepers before work can be carried out.
- Generally, high-altitude work platforms should first lift the lower arm, then the middle arm, and finally the upper arm. During the rotation operation of the lifting platform, it is necessary to raise the lower arm to a certain height before turning. The rotation should be slow, and attention should be paid to whether the distance between the scissor arm and the platform to each equipment meets safety requirements.
- Operators on the work platform should wear safety belts. When working in electrified areas, the vehicle body should be grounded according to regulations. The high-altitude operation of the lifting platform should be commanded by the person in charge, who should contact the lifting platform operator according to the signal specified in GB5082 standard. The signal emitted must be clear and accurate.
- Before conducting platform operations, the person in charge of the work should provide technical and safety instructions to the operators, including: job content and requirements; Safety precautions and danger points; Personnel division of labor and scope of responsibility. The person in charge of the work should not only inspect the condition of the vehicle and the operators, but also be responsible for checking whether the terrain environment, takeoff and landing comply with the requirements of safety technical measures or the pre formulated work plan. If there are any discrepancies, corresponding measures should be formulated before starting work.
Matters Needing Attention
- Any work carried out at a height of 2 meters (most domestic standards are 1.8 meters) or above should be considered as high-altitude operations. Any work that can be done in advance on the ground must be done on the ground to minimize high-altitude operations.
- Personnel engaged in high-altitude work must be physically healthy. Those who suffer from mental illness, epilepsy, or have been identified by a physician as having hypertension, heart disease, or other diseases that are not suitable for high-altitude work are not allowed to participate in high-altitude work. It is prohibited to work at heights when it is found that staff members are drinking alcohol or feeling lethargic.
- Personnel working on high-altitude work platforms must receive guidance on relevant equipment or be familiar with the equipment operation specifications and safety precautions for high-altitude work platform equipment in the “High Altitude Work Platform Operation Manual” before they can carry out high-altitude work.
- When working on the dam crest, steep slopes, roofs, cliffs, towers, suspension bridges, and other dangerous edges, safety nets or protective railings should be installed on the side facing the air. Otherwise, workers must use safety belts.
- Ice, snow, gravel, and soil on steep cliffs, slopes, or sidewalks must be regularly cleaned, and a 1-meter high railing must be installed on the outer side. Install 18 centimeter high side panels or soil ridges on the inner side of the railing to prevent falling objects from injuring people.
- When working on scaffolding without scaffolding or without railings, if the height exceeds 1.5 meters, safety belts must be used or other reliable safety measures must be taken.
- The seat belt should be inspected before use and a static load test should be conducted regularly (every 6 months). The test load is 225 kilograms and the test time is 5 minutes. After the test, check for any deformation, breakage, etc., and keep test records. Unqualified seat belts should be dealt with promptly.
- The hook or rope of the seat belt should be hung on a sturdy and sturdy component or on a steel wire rope specifically designed for hanging seat belts. Prohibit hanging on moving or unstable objects.
- All high-altitude work should use tool bags. Larger tools should be tied to sturdy components with ropes and should not be placed randomly to prevent accidents from falling from heights.
- When working at heights, except for relevant personnel, no one is allowed to walk or stay below the workplace. Fences or other protective devices should be installed below the workplace to prevent falling objects from injuring people. If working on a grid like platform, wooden boards should be laid to prevent tools and equipment from falling off.
- Tools and materials are not allowed to be thrown up and down. They should be securely tied with ropes and then lifted down or up to avoid injuring workers below or damaging scaffolding.
- When working simultaneously at the upper and lower levels, a tight and sturdy protective partition, canopy or other isolation facilities must be erected in the middle, and workers must wear safety helmets.
- When working outdoors at heights below minus ten degrees Celsius in winter, it is necessary to set up a heating rest area near the construction area, and the heating equipment should be managed by a dedicated person, paying attention to fire prevention.
- In case of strong wind of level 6 or above, rainstorm, thunder, fog and other severe weather, outdoor work at heights shall be stopped.
- It is prohibited to work on unstable structures (such as asbestos tile roofs). To prevent accidental login, warning signs should be hung at necessary locations of this structure.
Safety Protection
Safety Hat
- Before using the safety helmet, check whether the shell, lining, and strap are complete and effective.
- Before using the safety helmet, adjust the lining of the helmet so that each part of the lining is spaced at a certain distance from the helmet shell.
- The hoops should be adjusted according to the shape of the person’s head to prevent the front of the hat from slipping and blocking the line of sight when working with the head down.
- It is strictly prohibited to merge the two layers of top lining of the safety helmet into one layer.
- The safety helmet should be worn tightly and upright, and the headband should be fastened under the jaw and fastened tightly.
- The validity period of safety helmets shall be calculated from the date of completion of product manufacturing. Plastic helmets shall not exceed two and a half years, and fiberglass helmets shall not exceed three and a half years.
Safety Belt
The seat belt must be inspected and approved by the inspection unit every six months before it can be used.
When working under the following conditions, seat belts should be fastened:
- When entering the workplace for work that may involve high-altitude operations, one must wear a safety belt;
- When working at heights exceeding two meters;
- When working on scaffolding without scaffolding or without barriers, with a height exceeding 1.5 meters;
- When working on sloping roofs;
- Flat roofed houses, when there is no protective fence within 1.2 meters from the edge or opening of the roof;
- Any suspended platform or workbench;
- On any scaffolding with incomplete guardrails or planks;
- On ladders near openings on the roof or ground;
- When there are no reliable fall prevention measures for high-altitude operations.
How to use seat belts correctly:
- To tighten the waist belt, the waist buckle component must be securely fastened and properly fastened;
- When using a safety belt for hanging operations, the hook should not be directly hooked onto the safety belt rope, but should be hooked onto the hanging ring of the safety belt rope;
- Prohibit hanging seat belts on components that are not secure or have sharp corners;
- Using the same type of seat belt, each component cannot be replaced without authorization;
- Seat belts that have been severely impacted cannot be used even if their appearance remains unchanged;
- It is strictly prohibited to use safety belts to transfer heavy objects;
- The seat belt should be securely and reliably hung above, with a height not lower than the waist.
Safety Rope
- To ensure the safety of high-altitude workers during movement, it is required to fasten the safety belt while hanging it on the safety rope when performing particularly dangerous operations.
- It is prohibited to use hemp rope as a safety rope.
- A buffer should be added when using a long rope of more than 3 meters.
- A safety rope cannot be used by two people at the same time.
Differential protector
- The self-locking device should be inspected before use.
- The self-locking hook should be hung on the metal ring of the seat belt.
- Self locking devices that have been severely impacted should be discontinued from use.